Femia > Health Library > Pregnancy > Pregnancy health > First trimester pregnancy diet: 1 to 3-month pregnancy diet chart and meal plans
First trimester pregnancy diet: 1 to 3-month pregnancy diet chart and meal plans

- Updated Feb 25, 2025
- Published
CRAFTED BY HUMAN
Crafted by human At Femia, we provide accurate and up-to-date information at every stage of your journey, from trying to conceive, pregnancy and postnatal support. All content is created by a real person based on in-depth research and own professional experience. Femia ensures that you will receive expert advice, strict accuracy and a personalized approach from our authors/medical experts. Learn more about our editorial policy.
FACT CHECKED
Fact checked At Femia Health, we maintain the highest standards of editorial excellence in delivering content focused on helping you conceive, guiding you through pregnancy, and supporting you postpartum. Explore our content review principles to learn how we ensure the accuracy and quality of our health and lifestyle tips for every stage of your journey.

Created with Hector Chapa, MD, FACOG, Clinical associate professor, Obstetrics and Gynecology Texas A&M University, College of Medicine in Bryan-College Station, USA
In addition to supplements prescribed by your healthcare provider, future moms should include essential nutrients like folic acid, iron, and calcium in their diet. Eating small, frequent meals; staying hydrated; and avoiding mercury-rich foods, raw meats, and excessive vitamin A can help manage pregnancy symptoms and lower health risks. Our 1 to 3 month pregnancy diet chart will guide you through the essential nutrients for this stage of pregnancy and those that can help mitigate risks such as certain birth defects, low birth weight, and maternal health issues.
The first trimester can be one of the most challenging times during pregnancy due to physical and hormonal changes. Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for your baby’s development and your well-being. Fortunately, strict diets aren’t necessary; you can enjoy a variety of foods while ensuring you get enough nutrients.
Proper nutrition at this stage is crucial for the following:
- Supporting the rapid cell division and fetus organ formation.
- Supporting the mother’s health, reducing the risk of anemia and gestational diabetes.
- Helping alleviate common pregnancy symptoms like nausea and fatigue.
👉Find out more: 10 weird pregnancy symptoms you didn’t know existed
@femia.fertility 5 key steps for a successful pregnancy journey: 🥗 Balance your diet 👟 Walk 8K steps daily 💧 Stay hydrated 🧘♀️ Meditate to relieve stress 🤸♀️ Do pelvic exercises Your dream of parenthood starts with taking care of YOU. Follow Femia for more on fertility-friendly nutrition, exercises, and meditation tips. #ttccommunity #pregnancyjourney #ttcjourney #fertilityjourney #fertilityapp #ultrasound #dreambaby #momtobe ♬ Beautiful Is You - Karissa Ella
Pregnancy diet: Focus on these essential nutrients
A nutritional diet doesn’t always mean eating only specific products. But, including foods that contain essential nutrients, like lean meats, yogurt, edamame, kale, beans, and bananas rich in the nutrients you need during the first trimester, is a good way to support your and your baby’s health. Below is a first trimester pregnancy food chart to help you figure out what foods you may want to consider including in your diet.

First month pregnancy food chart

The first month of pregnancy sets the stage for the following months. That’s why it is the best time to improve your nutrition. Here is the list of nutrients to focus on for the first month:
| Nutrient | Source | Advantage | Recommended intake |
|---|---|---|---|
| Folic acid | Leafy vegetables, legumes, fortified cereals. | Fetal development requires folate to make healthy new cells and DNA as key cell-building blocks. Folate also helps to form normal red blood cells and amino acids.
| 400–800 micrograms per day. |
| Iron | Lean meats, spinach, beans. | Pregnant women require more iron and folic acid to meet both their and their baby's nutritional needs. Lack of iron during pregnancy may have potential negative impacts on the mother’s health, causing pregnancy complications and fetal development. | 1,040mg per day. |
| Calcium | Dairy products, fortified plant milks, leafy greens. | Calcium is essential for the healthy development of a baby's bones and teeth. It also boosts muscle, heart, and nerve development. | 800mg per day. |
| Protein | Lean meats, eggs, dairy, legumes. | Additional protein is essential for a healthy pregnancy, as the expansion of blood volume and growth of the maternal tissues require more protein. | A minimum of 60g of protein per day, accounting for about 20–25% of the calorie intake. |
| Omega-3 | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts. | Adequate consumption of omega-3 fatty acids is vital for a baby's brain and retina development. Omega-3 fatty acids may also be helpful in determining the length of gestation and preventing postpartum depression. | 650mg per day. |
Second month pregnancy food chart

Your baby at this stage is still very small and starting to develop a digestive tract, eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. Keeping all the nutrients mentioned above, you may also want to add the following foods into your diet during the second month of pregnancy:
| Nutrient | Source | Advantage | Recommended intake |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | Fortified dairy products, fatty fish, egg yolks, sunlight exposure. | Vitamin D is crucial for the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, supporting the baby's bone development. It also boosts the mother's immune system and mood. | 600 international units (IU) per day. |
| Fiber | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes. | Fiber helps maintain a healthy digestive system and prevent constipation, which may occur during pregnancy. It also helps control blood sugar levels. | 25–30g per day. |
| Vitamin E | Sunflower seeds, raw almonds. | Vitamin E, when combined with vitamin C, can be helpful in reducing the risks of miscarriage and preeclampsia—high blood pressure that may occur in some pregnant women. | 22–30mg per day. |
👉Find out more: 10 weird pregnancy symptoms you didn’t know existed
Third month pregnancy food chart
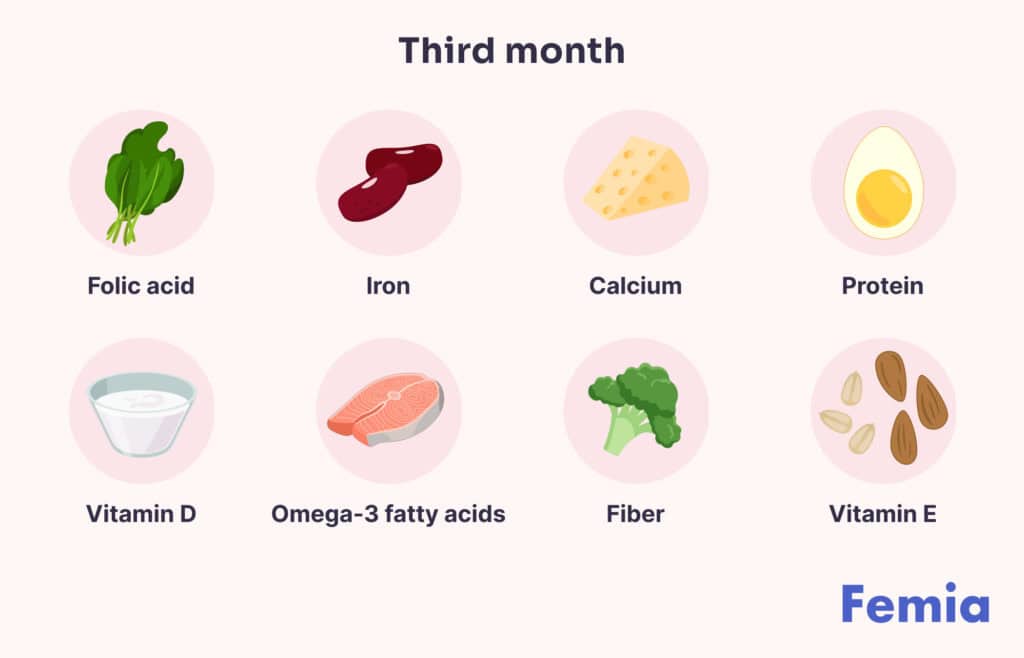
By the end of the third month, all of your baby’s major organs are formed. They also have arms, hands, unique fingerprints, feet, and toes. Your baby can also open and close its fists and mouth.
You are now probably feeling better, with the nausea gone and more energy than in the previous two months.

Nutritional needs during the third month of pregnancy are the same as with two previous ones, the only difference is that the dosage may differ. Please always consult a healthcare professional to identify your nutritional requirements and get personal guidance on recommended dosage.
First trimester meal plan
Now, let’s explore a detailed first trimester pregnancy meal plan with the above-mentioned nutrients.

| Meal | Meal options |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal topped with fresh berries and a drizzle of honey.
Smoothie made with spinach, banana, Greek yogurt, and a splash |
| Snack | Nuts such as almonds or walnuts.
Yogurt with granola and sliced fruits. |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, and a lemon vinaigrette.
Lentil soup with a side of whole grain bread. |
| Snack | Carrot sticks with hummus.
|
| Dinner | Baked salmon with a side of steamed broccoli, and brown rice.
Spaghetti with marinara sauce, and a side of roasted |
| Snack | Milk with a dash of cinnamon.
Bowl of berries with a spoonful of Greek yogurt. |
What fruits are beneficial during pregnancy and why?
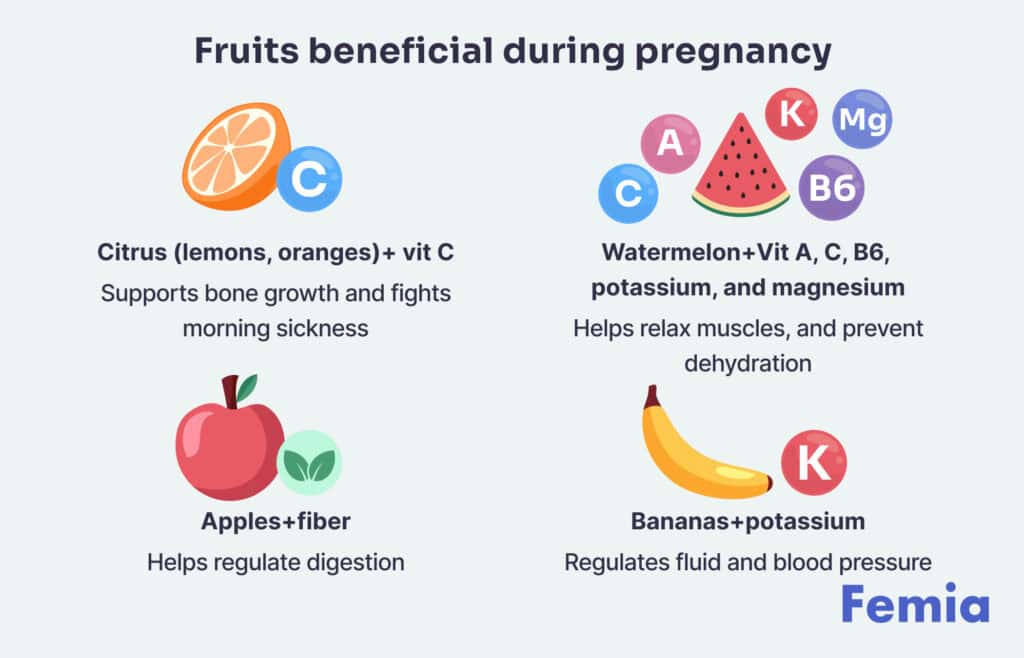
Expecting mothers may consider adding some fruits to their diet as a snack, since some well-known fruits are rich in essential nutrients and can help support the baby’s and mother’s health during the entire pregnancy journey. Here is a pregnancy fruit chart for the first trimester:
- Apples: high in fiber, which helps regulate a woman’s digestion and prevent hemorrhoids.
- Citrus: opt for lemons and oranges, since they are high in vitamin C, which is responsible for helping your baby’s bones grow properly. Citrus is also effective in fighting morning sickness during pregnancy.
- Bananas: they contain a lot of potassium, which helps regulate the fluid and blood pressure in a woman’s body.
- Watermelon: as a superfood, watermelon is rich in vitamins A, C, B6, potassium, and magnesium. Watermelon helps relax muscles, fight morning sickness, and prevent dehydration.
👉Find out more: Twin pregnancy belly week by week: What to expect

Tips for a healthy first trimester diet
Don’t worry if you can’t always meet your dietary needs or make healthy daily food choices. Sometimes, pregnancy complications like fatigue, morning sickness, and food aversions make eating a nutritious diet incredibly hard. Here are a few ways you can consider to reach your goals a bit more easily:
1. Stay hydrated
Aim for at least 8–10 glasses of water a day. If you can’t drink enough water, you can also drink other beneficial fluids like herbal teas, milk, and diluted fruit juices.
2. Eat small, frequent meals
Managing nausea is easier when you eat small, frequent meals instead of three large ones. That is because this helps keep blood sugar levels stable. So you may want to consider adding bland, easy-to-digest foods like crackers, toast, and bananas to your diet for easy snack options throughout the day.
3. Limit caffeine intake
It is best to reduce caffeine consumption to less than 200 mg per day, which is about one 12-ounce cup of coffee. You can also choose healthier sources of caffeine like tea, including green, matcha, and Earl Grey tea.
4. Include fiber-rich foods
These may include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, which help prevent constipation. Foods like apples, berries, broccoli, beans, and whole-grain bread are great sources of fiber.
👉Find out more: Understanding weight loss during pregnancy

Foods to avoid during the first trimester
During the first trimester, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced and safe diet, focusing on nutrient-dense foods and avoiding those that could pose risks to your developing baby.
Aside from foods on the list, it is best to consult a doctor to verify what products are not recommended in your case. Here is a general list of products to avoid during pregnancy:
| Food to avoid | Reasoning |
|---|---|
| Foods high in mercury | Fish like swordfish, shark, king mackerel, and tilefish could be harmful to your baby's growing nervous system. That's why it is best to opt for low-mercury fish like salmon, catfish, shrimp, and canned light tuna. |
| Raw or undercooked seafood | Sushi, sashimi, ceviche, and raw oysters can contain harmful bacteria and parasites that can lead to infections like listeriosis and toxoplasmosis. |
| Undercooked or raw meat and poultry | Rare steaks, undercooked hamburgers, and pink poultry may harbor bacteria like E. coli, Salmonella, and Listeria, so it is best to avoid both raw and undercooked meat. |
| Alcohol | According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), there is no known safe amount of alcohol to consume during pregnancy. This includes any amount or type of alcohol and applies to every stage of pregnancy, even before a woman knows she is pregnant. |
| Excessive vitamin A | Vitamin A is crucial for mother's health, but consuming an excessive amount through multivitamins or supplements may lead to birth defects. |
Questions from the Femia community
Can I maintain my vegetarian/vegan diet when pregnant?
Even though plant-based diets may cause the risk of nutritional deficiencies such as proteins, iron, iodine, omega-3, and vitamin B12, modern evidence shows that well-planned vegetarian and vegan diets crafted by specialists may be considered safe during pregnancy.
Can I eat a low-carb diet when pregnant?
Going on a low-carb diet during pregnancy can affect your baby's weight and development. A woman's body needs more nutrients and food to support two organisms, so consulting a healthcare provider is essential to ensure you can maintain both your and your baby's health.
Can I take supplements instead of eating certain foods?
Supplements are a good choice when a future mother can't get enough nutrients from a typical diet. However, in most cases, it is best to have a nutritional diet and use supplements to fill gaps. Always consult your healthcare provider before taking any supplements.
How much weight should I gain in the first trimester?
Weight gain can vary, but usually women gain about 1 to 4.5 pounds during the first trimester. It is best to focus on having a nutritional diet instead of tracking weight gain closely.
Is it normal to have food aversions during the first trimester?
Yes, many women experience food aversions, especially during the first trimester. You can find healthy alternatives that you can tolerate.
The bottom line
Eating enough nutrients during pregnancy is crucial for ensuring your health and the health of your growing baby. Consider adding foods from our chart for a one- to three-month pregnancy meal plan to ensure your diet is well-balanced and rich in all the microelements your body needs. Remember that no diet is perfect, and it’s okay to have cravings and treat yourself with something delicious from time to time. Please always consult with a doctor to get personalized recommendations.
References
- Cleveland Clinic. “First Trimester of Pregnancy: What to Expect.” Cleveland Clinic, 22 Aug. 2022, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9699-first-trimester.
- Mayo Clinic. “First Trimester Pregnancy: What to Expect.” Mayo Clinic, 2017, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/pregnancy/art-20047208.
- Greenberg, James A, et al. “Folic Acid Supplementation and Pregnancy: More than Just Neural Tube Defect Prevention.” Reviews in Obstetrics & Gynecology, vol. 4, no. 2, 2011, pp. 52–59, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3218540/.
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Nutritional Status During Pregnancy and Lactation. “Iron Nutrition during Pregnancy.” Nih.gov, National Academies Press (US), 2016, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK235217/.
- “Background.” Www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, World Health Organization, 2013, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK154181/.
- Lactation, Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Nutritional Status During Pregnancy and. Protein and Amino Acids. Www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, National Academies Press (US), 1990, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK235221/.
- Coletta, Jaclyn M, et al. “Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Pregnancy.” Reviews in Obstetrics and Gynecology, vol. 3, no. 4, 2010, pp. 163–171.
- Mithal, Ambrish, and Sanjay Kalra. “Vitamin D Supplementation in Pregnancy.” Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, vol. 18, no. 5, 2014, pp. 593–6, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4171878/,https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-8210.139204.
- Pretorius, Rachelle A., and Debra J. Palmer. “High-Fiber Diet during Pregnancy Characterized by More Fruit and Vegetable Consumption.” Nutrients, vol. 13, no. 1, 24 Dec. 2020, p. 35, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010035.
- Roberts, James M., et al. “Vitamins c and E to Prevent Complications of Pregnancy-Associated Hypertension.” New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 362, no. 14, 8 Apr. 2010, pp. 1282–1291, https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa0908056.
- Cleveland Clinic. “Fetal Development.” Cleveland Clinic, 3 Mar. 2023, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7247-fetal-development-stages-of-growth.
- Oyenihi, Ayodeji B., et al. ““An Apple a Day Keeps the Doctor Away”: The Potentials of Apple Bioactive Constituents for Chronic Disease Prevention.” Journal of Food Science, vol. 87, no. 6, 3 May 2022, https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.16155.
- Lv, Xinmiao, et al. “Citrus Fruits as a Treasure Trove of Active Natural Metabolites That Potentially Provide Benefits for Human Health.” Chemistry Central Journal, vol. 9, no. 1, Dec. 2015, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-015-0145-9.
- Quan, Zilin, et al. “Effect of Banana Intake on Serum Potassium Level in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” International Journal of Nursing Sciences, 14 Mar. 2024, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352013224000334, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2024.03.016. Accessed 17 Apr. 2024.
- Naz, Ambreen, et al. “Watermelon Lycopene and Allied Health Claims.” EXCLI Journal, vol. 13, 3 June 2014, pp. 650–660, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4464475/#:~:text=Additionally%2C%20watermelon%20is%20rich%20source.Accessed 25 June 2024.
- Mayo Clinic Staff. “Water: How Much Should You Drink Every Day?” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Clinic, 14 Oct. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/water/art-20044256.
- Mayo Clinic. “Pregnancy and Fish: What’s Safe to Eat?” Mayo Clinic, 2019, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/pregnancy-and-fish/art-20044185.
- “Eating Raw, Undercooked, or Cold Meats and Seafood.” PubMed, Organization of Teratology Information Specialists (OTIS), 1994, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK582930/.
- “Do You Know Which Foods to Avoid When You’re Pregnant?” Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/pregnancy-nutrition/art-20043844#:~:text=Don.
- Armstrong, Elizabeth Mitchell. “Making Sense of Advice about Drinking during Pregnancy: Does Evidence Even Matter?” The Journal of Perinatal Education, vol. 26, no. 2, 2017, pp. 65–69, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6353268/, https://doi.org/10.1891/1058-1243.26.2.65.
- Abadie, Raegan B, et al. “Vitamin A-Mediated Birth Defects: A Narrative Review.” Cureus, 14 Dec. 2023, https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.50513.
- Sebastiani, Giorgia, et al. “The Effects of Vegetarian and Vegan Diet during Pregnancy on the Health of Mothers and Offspring.” Nutrients, vol. 11, no. 3, 6 Mar. 2019, p. 557, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6470702/, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030557.
- Tanner, Helen, et al. “Consumption of a Low Carbohydrate Diet in Overweight or Obese Pregnant Women Is Associated with Longer Gestation of Pregnancy.” Nutrients, vol. 13, no. 10, 5 Oct. 2021, p. 3511, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8538994/, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103511.
- Kominiarek, Michelle A., and Priya Rajan. “Nutrition Recommendations in Pregnancy and Lactation.” Medical Clinics of North America, vol. 100, no. 6, Nov. 2016, pp. 1199–1215, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5104202/, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2016.06.004.
- Mayo Clinic. “Pregnancy Weight Gain: What’s Healthy?” Mayo Clinic, 2017, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/pregnancy-weight-gain/art-20044360.
- Yalew, Abel, et al. “Food Aversion during Pregnancy and Its Association with Nutritional Status of Pregnant Women in Boricha Woreda, Sidama Regional State, Southern Ethiopia, 2019. A Community Based Mixed Crossectional Study Design.” Reproductive Health, vol. 18, no. 1, 18 Oct. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-021-01258-w. Accessed 5 Nov. 2021.
- Merrell, Brigham J., and John P. McMurry. “Folic Acid.” PubMed, StatPearls Publishing, 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554487/#:~:text=The%20World%20Health%20Organization%20recommends.
- Lactation, Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Nutritional Status During Pregnancy and. “Iron Nutrition during Pregnancy.” Www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, National Academies Press (US), 1990, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK235217/#:~:text=In%20addition%2C%20about%20450%20mg.
- Willemse, Jessica P. M. M., et al. “Calcium Intake from Diet and Supplement Use during Early Pregnancy: The Expect Study I.” European Journal of Nutrition, vol. 59, no. 1, 2020, pp. 167–174, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7000487/, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-01896-8.
- Kominiarek, Michelle A., and Priya Rajan. “Nutrition Recommendations in Pregnancy and Lactation.” Medical Clinics of North America, vol. 100, no. 6, Nov. 2016, pp. 1199–1215, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5104202/, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2016.06.004.
- Greenberg, James A, et al. “Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation during Pregnancy.” Reviews in Obstetrics and Gynecology, vol. 1, no. 4, 2008, pp. 162–169, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2621042/#:~:text=Two%20servings%20of%20fish%20per. Accessed 25 June 2024.
Learn about cervical checks during pregnancy, including what to expect, when they typically happen, and how they can help monitor your progress.

A coregasm is an exercise-induced orgasm that occurs during an intense core workout. An orgasm while working out is an asexual bodily response to exercise.
Learn about first-trimester screening tests, including how they’re performed, what they screen for, and what the results can indicate. Understand the process and what to expect during early pregnancy.
