Femia > Health Library > Pregnancy > Pregnancy health > Understanding weight loss during pregnancy
Safe weight loss during pregnancy: What to know and when to consult a doctor
- Updated Feb 10, 2025
- Published
CRAFTED BY HUMAN
Crafted by human At Femia, we provide accurate and up-to-date information at every stage of your journey, from trying to conceive, pregnancy and postnatal support. All content is created by a real person based on in-depth research and own professional experience. Femia ensures that you will receive expert advice, strict accuracy and a personalized approach from our authors/medical experts. Learn more about our editorial policy.
FACT CHECKED
Fact checked At Femia Health, we maintain the highest standards of editorial excellence in delivering content focused on helping you conceive, guiding you through pregnancy, and supporting you postpartum. Explore our content review principles to learn how we ensure the accuracy and quality of our health and lifestyle tips for every stage of your journey.
Weight loss during pregnancy is relatively common and may happen due to hormonal fluctuations, increased calorie use by the baby, changing eating habits, metabolic rate change, and morning sickness.
However, significant or prolonged loss may also cause concern and require personalized guidance from your healthcare provider.
Losing some weight during pregnancy can happen due to a range of normal and unconcerning reasons. On the other hand, weight loss during pregnancy might also signal some emerging issues.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the main reasons for weight loss in every trimester to help you understand what is happening to your body and if it’s okay. We will also discuss potential concerns that may indicate the need for a consultation with a doctor.
Track your symptoms with Femia and get tailored
health advice right on your phone
Can you lose weight during pregnancy safely?
Yes, it’s possible to lose weight during pregnancy safely, but it depends on various factors like the trimester, pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), and the cause of weight loss. In many cases, mild weight loss is normal, particularly in the first trimester due to morning sickness. However, significant or prolonged weight loss requires close monitoring and guidance from your healthcare provider. Using a pregnancy weight gain calculator can help track changes and support healthy weight management during pregnancy.
@femia.fertility If you struggle with food cravings during PMS and want to eat more than you need, save these tips to help you manage the situation. #cravings #pregnancycravings #pmscravings #ttc #periodtok #pmssymptoms #pregnancysymptoms #healthynutrition ♬ original sound - Femia fertility tracker
Weight loss in each trimester: What’s normal and what’s not
First trimester: Why morning sickness causes weight loss
Most women face morning sickness around 4–7 weeks, and it settles around the end of your first trimester and beginning of the second, though there might be variations. Nausea often curbs your appetite and makes it hard to consume the amount of calories your body needs, while vomiting can cause you to lose your calories.
If you aren’t consuming the calories necessary for the baby’s growth, your body will likely pick up those calories and nutrients from your own fat reserves to make up the deficit. Hence, you may see a lower number on the scales.
👉Find out more: First trimester pregnancy diet: 1 to 3-month pregnancy diet chart and meal plans
Second trimester: Metabolism and dietary changes
The second trimester is when active weight gain typically begins, as your baby starts growing and developing very rapidly. At this stage, you need to understand the deep metabolic changes that happen in your body, as well as your previous BMI and eating habits, to answer the main question of “Why am I losing weight during pregnancy 2nd trimester?”
The basal metabolic rate change might be the first reason. It starts increasing around the end of your first trimester and may double during the second and third trimesters. The metabolism increase is an individual factor affected by the size of the fetus, the mother’s activities, etc. Due to an increased metabolism, it’s generally recommended that expectant mothers increase their daily calorie intake by around 340 calories. If the intake stays the same or reduces, there might be weight loss.
New dietary habits might also cause weight loss. A pregnancy diet should typically consist of lots of fruits, vegetables, starchy food, proteins, and other important nutrients. Switching to such healthy eating habits can make overweight mothers-to-be expend their pre-pregnancy fat reserves to support their baby’s growth, which may lead to weight loss.
Weight concerns in the third trimester
At later phases of the third trimester, females might arrive at the end of their pregnancy-induced weight gain and experience stabilization or even mild weight loss. By this time, many women get so accustomed to weight gain that seeing the number on the scales drop may feel confusing and somewhat unsettling.
In fact, maintaining a stable weight or losing some pounds is relatively common at this stage. It’s a signal that your body is getting ready for labor and can be explained by the following reasons:
- Amniotic fluid. The amount of fluid in the uterus typically decreases during the final days of pregnancy, which causes weight loss.
- Bowel movements. At the end of the third trimester, some women experience more frequent and loose bowel movements, which reduces the amount of liquid in their body.
- Urination. It may also become more frequent, as the baby’s head adds more pressure on your bladder. Fluids exit your body at a higher rate and may decrease your weight.
- Appetite. You might notice it declines due to increasing discomfort and anxiety before labor.
- Fluid reduction. When the due date is close, your body doesn’t need to store as much fluid as during the pregnancy and might naturally reduce fluid retention. While heightened perspiration can contribute to fluid loss, it is not always confirmed by medical sources as a primary cause. Usually, fluid is lost through other mechanisms, such as a reduction in the volume of amniotic fluid and increased urination.
- Nesting. The nesting instinct may also contribute to weight loss during the third trimester—a natural desire to create a safe and comfortable environment for your newborn can make you get on the move and burn more calories. However, this claim has limited scientific backing. While “nesting” might encourage increased activity, its impact on weight is minimal and not consistently observed.
It’s important to keep an eye on your weight fluctuations and contact your healthcare provider if concerned about losing too much weight.

Track your symptoms with Femia and get tailored
health advice right on your phone
Causes of weight loss during pregnancy
Weight loss during pregnancy can occur due to several reasons:
- Morning sickness: Nausea and vomiting reduce calorie intake, causing weight loss.
- Metabolism changes: An increased basal metabolic rate means your body burns more calories, leading to weight loss if calorie intake doesn’t increase.
- Dietary adjustments: Switching to healthier eating habits can result in weight loss, especially in women with higher BMIs.
- Stress and anxiety: Emotional factors can contribute to unintentional weight loss.
These causes are often harmless, but it’s important to ensure your weight loss isn’t excessive or prolonged.
Is it dangerous to lose weight in pregnancy?
Losing weight during pregnancy can be concerning, especially if your pre-pregnancy BMI is within a healthy range or lower. For women with a higher BMI, mild weight loss may be less worrisome. However, rapid or prolonged weight loss can pose risks to both mother and baby, particularly in terms of nutrient deficiencies.
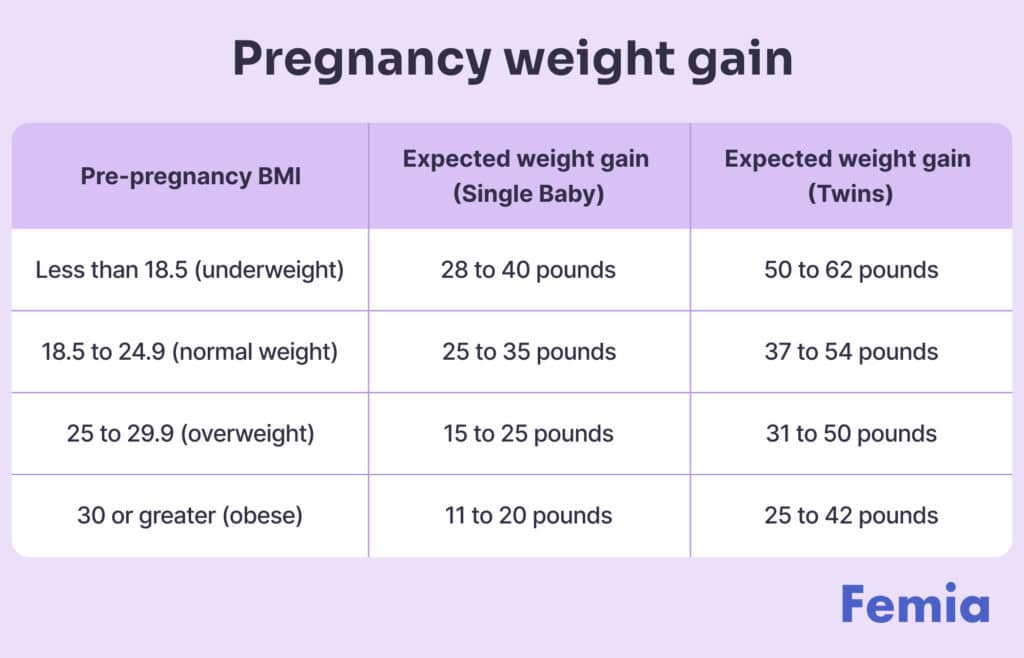
Safe ways to maintain a healthy weight during pregnancy
Maintaining a healthy weight during pregnancy is crucial for the well-being of both mother and baby. Here are practical tips to help prevent weight loss and support your body during pregnancy:
Practical tips for preventing weight loss during pregnancy
- Balanced diet: Focus on a nutrient-rich diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and proteins. Include healthy fats to meet calorie requirements.
- Small, frequent meals: If morning sickness is an issue, try eating smaller meals throughout the day to maintain your energy levels and nutrient intake.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and hydrating fluids like soups or herbal teas.
- Safe exercises: Engage in light physical activities, such as walking or prenatal yoga, to keep your body strong and energized.
- Managing morning sickness: Ginger tea, small snacks like crackers, and taking prenatal vitamins before bed can help ease nausea.
When to consult a doctor
If you were wondering “Is it normal to lose weight during pregnancy?”, now you see that there are natural and common reasons your weight might go down in every trimester. If it’s inconsistent and mild, there might be no reason to worry.
However, consider talking to your healthcare provider on the following occasions:
- Your weight loss is too swift and consistent;
- You feel weak and lack energy;
- You experience adverse effects of weight loss, such as feeling cold or dizzy;
- You can’t find relief for your nausea or vomiting.
These signs might signal potential complications that should be addressed by a doctor, especially later in your pregnancy. Even if you don’t experience any of these signals but are generally concerned about your weight gain or loss patterns, it might be a good idea to consult a doctor to ensure your and your baby’s safety.
Remember about the importance of regular prenatal check-ups. If you stick to a consistent prenatal care schedule, it will help your doctor track your weight fluctuations, detect any potential issues early on, and provide you with personalized medical guidance for your and your baby’s wellness.
Questions from the Femia community
Can I diet to lose weight while pregnant?
It’s generally not recommended to diet to lose weight during pregnancy. Expectant mothers need to receive extra nutrients and energy to support a healthy baby’s development. Instead of putting effort into losing or maintaining a specific weight, you should aim to develop a healthy and balanced diet that supplies your body with all the elements necessary for your and your baby’s health and safety. If there are any concerns about your diet or weight during pregnancy, consider talking to your healthcare provider. They will help you develop a personalized plan that will help you maintain a healthy weight and ensure that you and your baby receive all the macroelements you need.
Why am I not gaining weight despite eating more?
To many women, seeing no weight gain during pregnancy despite eating more can feel somewhat frustrating and disturbing, but there might be multiple reasons for it. The most common reasons include hormonal changes, increased metabolism, changed dietary habits, and increased caloric expenditure caused by the baby’s growth. Morning sickness might also cause weight loss. To ensure optimal health and give your baby enough support to grow and develop, it’s important to keep an eye on your weight and consult a doctor in case of any concerns.
Can losing weight during pregnancy harm the baby?
Weight loss during pregnancy can be natural. Losing a few pounds is common in the first trimester due to nausea and vomiting. However, weight loss might be more concerning in the second and third trimesters. While it may not always mean harm to the baby, it’s important to see your healthcare provider if there is significant or prolonged weight loss, because it might affect the baby’s health by not providing adequate nutrition for growth. A professional should be able to objectively assess your unique situation and help you stay on the right track with your nutrition and weight gain.
Are there specific dietary recommendations for preventing weight loss during pregnancy?
Yes - sticking to a healthy and balanced diet is the core recommendation for preventing weight loss. A pregnancy diet should focus on nutritious foods rich in vitamins and minerals necessary for the baby’s development. It should include lots of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. For nausea-induced weight loss, it’s recommended to have small, frequent meals to manage sickness and ensure that you consume enough nutrients. Staying hydrated is important for helping your body function properly, and taking prenatal vitamins can help fill nutritional gaps. If you are facing challenges with proper nutrition or are concerned about your weight, your healthcare provider can offer personalized guidance.
The bottom line
Weight loss during pregnancy is relatively common, though it often feels unsettling for mothers-to-be. Weight fluctuations may happen naturally during pregnancy because of hormonal changes, morning thickness, increased metabolism, and other factors. There also might be individual factors, such as pre-conception BMI and eating habits that can affect your weight patterns.
After reading this guide, you should know more about weight fluctuations and their reasons. Now, you see that these changes can take place in every trimester and do not necessarily mean something bad, though weight loss might be more concerning during the second and third trimesters. In order to make your pregnancy healthy, it’s important to monitor your weight, have regular prenatal check-ups, and turn to your healthcare provider in case of any concerns.
References
- “Weight gain in pregnancy.” The National Health Service (NHS). https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/related-conditions/common-symptoms/weight-gain/#:~:text=Weight%20gain%20in%20pregnancy%20varies,after%20your%20baby%20is%20born.
- LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA.”Managing your weight gain during pregnancy.” MedlinePlus, 21, Nov. 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000603.htm.
- Esa Davis MD, MPH, Christine Olson PhD. “Gestational Weight Gain” from “Primary Care: Clinics in Office Practice.” ScienceDirect, 2009. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/gestational-weight-gain.
- Pat Bailey. “Fat in Mom’s Milk Linked to Body Fat.” UCDAVIS, 30, Apr. 1993. https://www.ucdavis.edu/news/fat-moms-milk-linked-body-fat.
- Lappas M, Lim R, Price S, Prendergast LA, Proietto J, Ekinci EI, Sumithran P. “Exploring the Relationship Between Maternal Circulating Hormones and Gestational Weight Gain in Women Without Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Study.” Int J Womens Health, 15, Jun. 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7305340/#:~:text=Increased%20food%20intake%20and%20weight,influence%20appetite%20and%20body%20weight.
- JoLyn Seitz. “You can have a happy and healthy plus-size pregnancy.” SanfordHealth, 18, Mar. 2022. https://news.sanfordhealth.org/womens/can-happy-healthy-plus-size-pregnancy/#:~:text=Your%20baby%20will%20still%20get,ll%20probably%20lose%20some%20weight.
- John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. “Hyperemesis gravidarum.” MedlinePlus. 1, Jan. 2023. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001499.htm.
- Lain KY, Catalano PM. “Metabolic changes in pregnancy.” Clin Obstet Gynecol, Dec. 2007. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17982337/.
- “Unintentional weight loss.” The National Health Service (NHS), 16, Feb. 2022. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/unintentional-weight-loss/.
- “Morning sickness.” The National Health Service (NHS). https://www.nhs.uk/start-for-life/pregnancy/morning-sickness/#:~:text=Morning%20sickness%20begins%20early%20in,the%20causes%20of%20morning%20sickness.
- John W. Huffman. “Metabolic changes,” in “Pregnancy,” in “The normal events of pregnancy.” Encyclopedia Britannica, 13, Jul. 2024. https://www.britannica.com/science/pregnancy/Prenatal-care-and-testing.
- Good Food Is Good Medicine. “Pregnancy diet: Common myths and what you should eat during your pregnancy.” UC Davis Health, 3, Mar. 2021. https://health.ucdavis.edu/blog/good-food/pregnancy-diet-common-myths-and-what-you-should-eat-during-your-pregnancy/2021/03.
- “Have a healthy diet in pregnancy.” The National Health Service (NHS), 21, Apr. 2023. https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/keeping-well/have-a-healthy-diet/.
- “IS END OF PREGNANCY WEIGHT LOSS NORMAL?” Gwinnett Ob/Gyn Associates. https://www.gwinnettobgyn.com/News/weight-loss-end-of-pregnancy.
Discover how to recognize the signs and stages of a real dilated cervix in pregnancy, what to expect at different stages, and when to consult your healthcare provider.

Discover what quickening is in pregnancy, when to expect it, and what it feels like. Learn how to monitor your baby’s first movements and when to consult your doctor about any concerns.
Learn what’s happening at 15 weeks pregnant, from fetal development and common symptoms to ultrasound insights and self-care tips.

