Femia > Health Library > Pregnancy > Pregnancy week by week > 3 Weeks pregnant: Symptoms, body changes, and fetal development
3 Weeks pregnant: Symptoms, body changes, and fetal development
- Updated Mar 4, 2025
- Published
CRAFTED BY HUMAN
Crafted by human At Femia, we provide accurate and up-to-date information at every stage of your journey, from trying to conceive, pregnancy and postnatal support. All content is created by a real person based on in-depth research and own professional experience. Femia ensures that you will receive expert advice, strict accuracy and a personalized approach from our authors/medical experts. Learn more about our editorial policy.
FACT CHECKED
Fact checked At Femia Health, we maintain the highest standards of editorial excellence in delivering content focused on helping you conceive, guiding you through pregnancy, and supporting you postpartum. Explore our content review principles to learn how we ensure the accuracy and quality of our health and lifestyle tips for every stage of your journey.
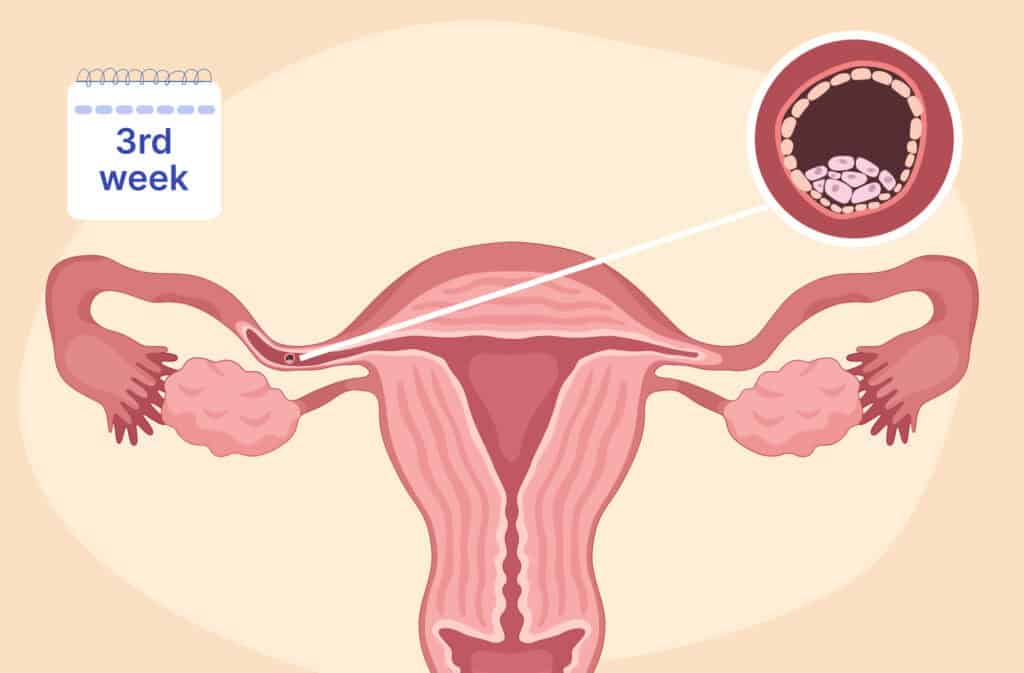
At 3 weeks pregnant, fertilization has likely taken place, and the fertilized egg—now called a zygote—is traveling through the fallopian tube toward the uterus. By the end of this week, the zygote may reach the uterus and begin the implantation process, transforming into a blastocyst. While this is a crucial stage in early pregnancy, most changes are happening at a cellular level, so noticeable symptoms are uncommon. Some people might experience very subtle signs due to early hormonal shifts, such as mild fatigue or heightened sensitivity to smells.
During the third week of pregnancy, a significant milestone occurs: fertilization. The zygote, a tiny cluster of rapidly dividing cells, is moving toward the uterus in preparation for implantation into the uterine lining.
Although hormonal changes are beginning, physical symptoms are usually minimal at this stage. Understanding this critical phase—when foundational cellular processes are setting the stage for pregnancy—can help you stay informed and prepared for the weeks ahead.
3-week pregnancy symptoms
At week 3 of pregnancy, most changes are happening on a microscopic level, and noticeable symptoms are uncommon. However, early hormonal shifts may cause very subtle signs that some people might begin to notice. Here’s what you might experience:
- Mild cramping: As the fertilized egg moves toward the uterus, you may feel slight cramping. Keep in mind that implantation—which can cause cramping and spotting—typically occurs at the end of this week or the beginning of week 4, so these symptoms might not appear just yet.
- Breast tenderness or swelling: At this early stage, hormone levels haven’t increased enough to cause significant changes in the breasts. If you do notice slight tenderness or swelling, it’s more likely associated with premenstrual syndrome (PMS) rather than early pregnancy symptoms.
- Increased discharge: Significant changes in vaginal discharge are unlikely at this stage. Any variations you notice are more likely due to the normal phase of your menstrual cycle rather than early pregnancy. Increased discharge, known as leukorrhea, typically occurs after implantation has been completed, which usually happens at the end of this week or the beginning of week 4.
- Fatigue and mood swings: Higher levels of progesterone can lead to fatigue, as well as mild mood changes, even before a missed period.
👉Find out more: 2 Weeks pregnant: What to expect in your body
Your body at 3 weeks pregnant
At 3 weeks pregnant, your body is experiencing very early hormonal changes. The fertilized egg, now a zygote or blastocyst, is moving from the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it will implant in the coming days. This early stage is crucial, as the body is building a supportive environment for the developing embryo.
3-week pregnant belly
At this stage, no visible changes in the belly occur. While the zygote is traveling toward the uterus, physical changes are minimal and generally not noticeable. Although hormonal changes begin after fertilization, their levels are still too low to cause significant physiological or visible effects. The major hormonal shifts that lead to noticeable symptoms usually start after implantation is complete. Therefore, any bloating or physical sensations are unlikely to be related to pregnancy at this point.
Baby development at 3 weeks of pregnancy
At week 3, fertilization has occurred, and the fertilized egg is now called a zygote. This zygote is not a single cell; it is already undergoing rapid cell division as it travels through the fallopian tube toward the uterus. By the end of this week, it transforms into a blastocyst, a cluster of cells consisting of two main parts: the inner cell mass that will develop into the embryo and the outer layer that will become the placenta after implantation is complete.
3-week ultrasound
An ultrasound at 3 weeks pregnant would not detect the embryo yet, as implantation has not occurred. Confirming pregnancy by ultrasound typically occurs around weeks 5-8, once a gestational sac is visible.
Fetus size at 3 weeks
The zygote at 3 weeks is still microscopic, about the size of a pinhead. Growth will accelerate in the coming weeks as cell division continues and major developmental stages begin.
👉Find out more:
4 Weeks pregnant: Symptoms, fetal size, and health tips
5 Weeks pregnant: A sneak peek into early baby development and symptoms
Health tips and self-care at 3 weeks pregnant
- Avoid harmful substances: Avoid alcohol, tobacco, and certain medications, as they can affect early fetal development.
- Prenatal vitamins: Continue taking prenatal vitamins, especially folic acid, to support neural development.
- Rest and hydration: With hormonal changes underway, getting enough rest and staying hydrated can support your energy levels.

Tips for 3 weeks pregnant
Get through the ‘two-week wait’
After tracking your cycle and timing intercourse around ovulation, you’re now faced with the ‘two-week wait’—the period between ovulation and the day your period is due. This can be a challenging and anxiety-inducing time for many women, as you wait to see if conception occurred. Instead of focusing on the wait, try to keep yourself distracted with activities you enjoy, like binge-watching a TV series, tackling projects around the house, or even starting a new hobby.
If you find the stress overwhelming, try calming activities like going for a walk, reading, or journaling your thoughts and feelings. Journaling can help you process any emotions that come up, and you can even use apps to track your feelings and any physical symptoms you experience. This period of waiting can feel long, but it’s a good time to relax and recharge before your pregnancy journey begins.
Pay attention to your emotions
It’s completely normal to feel anxious when you’re waiting for the results of a pregnancy test or just finding out you’re pregnant. If you’re feeling overwhelmed or worried, talking it out with your partner or a close friend can be helpful. Journaling your thoughts can also be an effective way to manage stress and clear your mind.
Avoid overheating
While it’s safe to enjoy warm baths, be cautious with hot tubs, saunas, and steam rooms during pregnancy. Overheating, especially in the early stages, has been linked to an increased risk of birth defects, so it’s important to keep your body temperature regulated.
Eat nutritious meals and snacks
Focus on consuming nutrient-rich foods to support your body’s needs. Include a variety of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Foods rich in vitamins and minerals like iron, calcium, and vitamin C are crucial. Healthy snack options, such as fruits, nuts, and yogurt, are also great for fueling your pregnancy.
Questions from the Femia community
What are the top questions to ask my OB-GYN?
Key questions might include nutrition guidance, managing symptoms, exercise recommendations, and what to expect in early pregnancy appointments.
When can I take a pregnancy test at 3 weeks pregnant?
Home pregnancy tests are typically more accurate after a missed period, around week 4, when hormone levels are detectable.
How can I support early pregnancy health at 3 weeks?
Maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and taking prenatal vitamins are all beneficial steps. At 3 weeks pregnant, as the zygote makes its journey toward the uterus, it’s a good time to start using an app to help track your pregnancy, even if the symptoms are subtle at this early stage.
The bottom line
At 3 weeks pregnant, fertilization has occurred, but physical signs of pregnancy may still be subtle. As the zygote te begins its journey toward implantation, early symptoms may appear, though they vary by individual. Taking care of your health with prenatal vitamins, rest, and a balanced diet will support a healthy pregnancy foundation.
References
- “3 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms & What to Expect.” BabyCenter, www.babycenter.com/pregnancy/week-by-week/3-weeks-pregnant.
- “Your Pregnancy and Baby Guide: Weeks 1 to 3.” NHS, www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/week-by-week/1-to-12/1-2-3-weeks/.
- “Week 3 of Pregnancy: Early Signs and Symptoms.” What to Expect, www.whattoexpect.com/pregnancy/week-by-week/week-3.aspx.

Discover how to distinguish pregnancy symptoms from common PCOS signs. Learn about missed periods, fatigue, nausea, and more, and get essential tips for managing PCOS during pregnancy.

Did you know your clitoris can be the key to unlocking your orgasm? Follow this guide for enhancing your clitoral satisfaction, and maximizing your sexual experience.
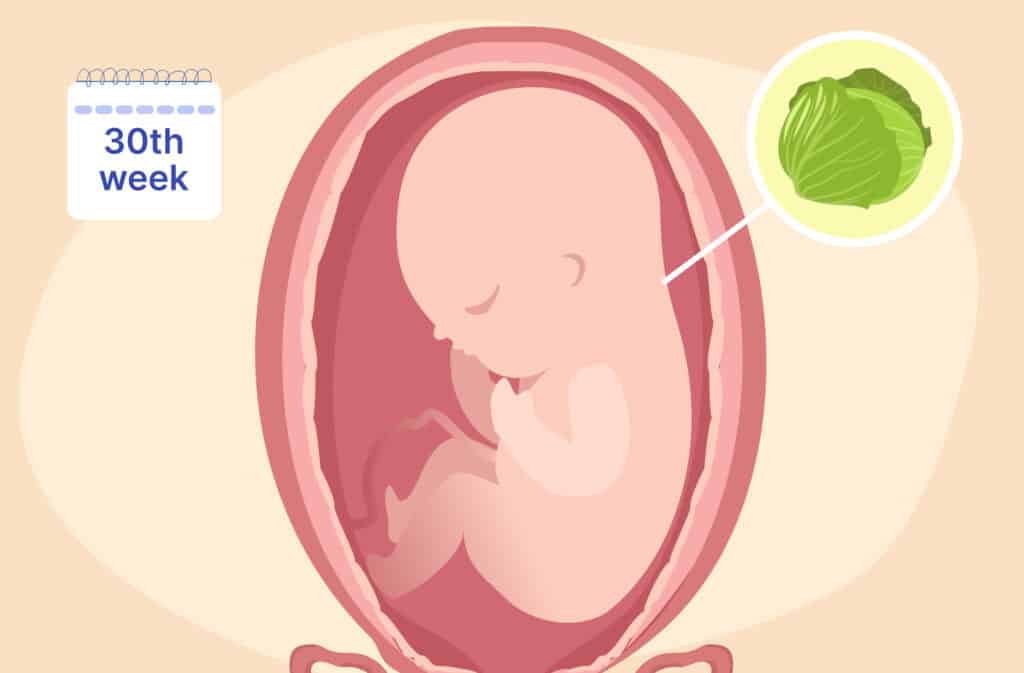

Discover what happens at 30 weeks pregnant, from baby’s development and weight gain tips to symptoms and labor prep.

