Femia > Health Library > Your cycle > Health > Fertility hormones: Essential female reproductive hormones and how to balance them for conception
Fertility hormones: Essential female reproductive hormones and how to balance them for conception
- Updated Feb 11, 2025
- Published
CRAFTED BY HUMAN
Crafted by human At Femia, we provide accurate and up-to-date information at every stage of your journey, from trying to conceive, pregnancy and postnatal support. All content is created by a real person based on in-depth research and own professional experience. Femia ensures that you will receive expert advice, strict accuracy and a personalized approach from our authors/medical experts. Learn more about our editorial policy.
FACT CHECKED
Fact checked At Femia Health, we maintain the highest standards of editorial excellence in delivering content focused on helping you conceive, guiding you through pregnancy, and supporting you postpartum. Explore our content review principles to learn how we ensure the accuracy and quality of our health and lifestyle tips for every stage of your journey.

Created with Hector Chapa, MD, FACOG, Clinical associate professor, Obstetrics and Gynecology Texas A&M University, College of Medicine in Bryan-College Station, USA
- The four main fertility hormones in females include FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone. The LH and FSH hormones are involved in ovulation, and progesterone and estrogen hormones prepare the uterine lining for the baby’s growth and development.
- An imbalance of fertility hormones can interfere with ovulation and affect the female’s ability to conceive.
- Lifestyle factors, like a healthy diet, moderate exercise, limiting smoking and alcohol and using certain supplements with the doctor’s recommendations, can help improve fertility and restore hormonal balance.
The four major female fertility hormones involved in the reproduction cycle include FSH, LH, estrogen and progesterone. The FSH and LH hormones help in ovulation (the release of egg from the female’s ovaries) and promote follicular growth. Estrogen and progesterone prepare the female’s uterine lining for implantation, making the body ready for conception.
A balance of all the fertility hormones is necessary for a healthy pregnancy to occur. Moreover, hormonal imbalance may disrupt the process of ovulation and fertilization and increase the risks of infertility. So, let’s discuss female hormones, how to balance hormones for fertility, hormone testing and healthy conception in detail.
Try Femia’s plan that helps remove your blocks to get pregnant
What are fertility hormones?
The female reproductive hormones, also known simply as “fertility hormones,” work together to stimulate ovulation and create a healthy environment in the female’s uterus for the embryo to grow and develop into a baby.
The four significant hormones, estrogen, progesterone, LH, and FSH, are released monthly to prepare the female’s body for pregnancy. If the pregnancy is successful, the body releases another hormone called the Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone, which is a strong indicator of a positive pregnancy.
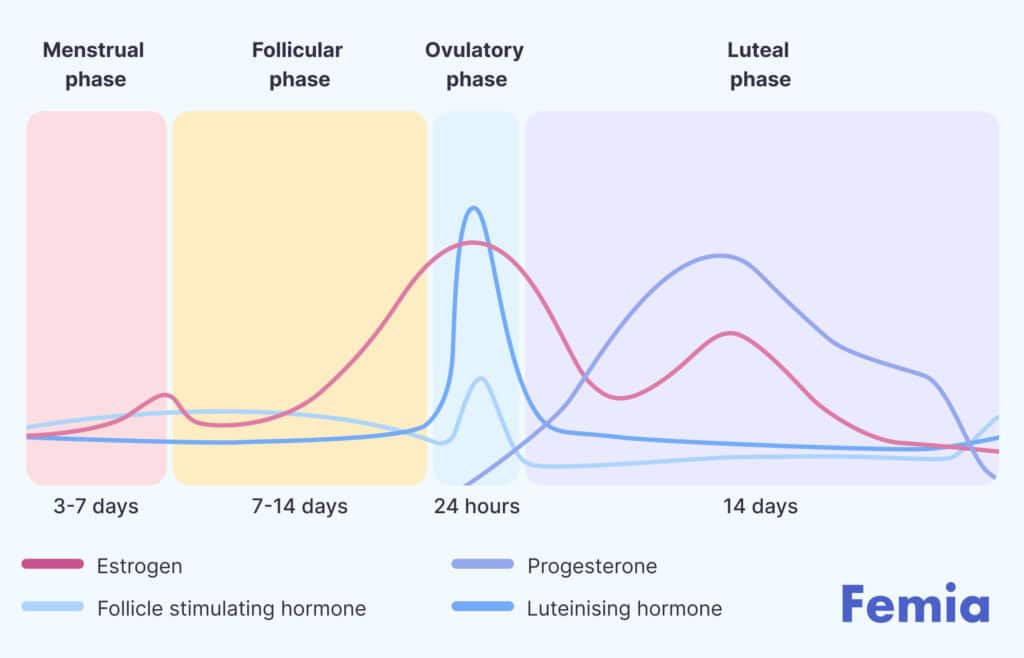
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) plays a vital role in female fertility by stimulating the ovaries to produce and mature eggs. It is key in the regulation of the menstrual cycle and ovulation process.
- Regulates ovulation: FSH stimulates the ovaries to produce and mature eggs.
- Indicator of fertility: High FSH levels can suggest reduced ovarian reserve, while low levels indicate healthy ovarian function.
- Increases with age: FSH levels naturally rise as a woman approaches menopause due to reduced ovarian function.
- Fertility testing: FSH levels are measured to assess ovarian reserve and help guide fertility treatments, such as IVF.
Estrogen
- Regulates the menstrual cycle: Estrogen helps regulate the growth and maturation of eggs in the ovaries and thickens the uterine lining for potential pregnancy.
- Supports ovulation: Rising estrogen levels during the follicular phase prepare the body for ovulation by triggering the release of luteinizing hormone (LH).
- Affects cervical mucus: Estrogen increases cervical mucus production, making it easier for sperm to travel to the egg.
- Fertility testing: Estrogen levels are often tested to assess ovarian function, determine ovulation, and monitor fertility treatments.
Luteinising hormone (LH)
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) is crucial for female fertility:
- Triggers ovulation: LH surge triggers the release of a mature egg from the ovary during the menstrual cycle.
- Regulates the luteal phase: After ovulation, LH helps in the formation of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone to maintain the uterine lining.
- Indicator of fertility: Low LH levels can suggest issues with ovulation, while high levels may indicate polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Fertility testing: LH levels are often measured to track ovulation and guide fertility treatments.
Progesterone
- Supports pregnancy: Progesterone helps prepare the uterine lining for implantation and supports early pregnancy by maintaining this lining after conception.
- Regulates the luteal phase: After ovulation, progesterone levels rise to prevent the release of additional eggs and to prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy.
- Prevents further ovulation: Progesterone inhibits the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) during pregnancy to prevent further ovulation.
- Fertility testing: Progesterone levels are measured to confirm ovulation and monitor the luteal phase, especially during fertility treatments.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
- Key to pregnancy detection: hCG is produced after implantation and is the hormone detected by home pregnancy tests.
- Supports early pregnancy: It helps maintain the corpus luteum, which in turn produces progesterone to sustain the pregnancy in its early stages.
- Indicates ovulation and pregnancy success: hCG levels rise rapidly in early pregnancy, and measuring these levels can help monitor the health of the pregnancy.
- Used in fertility treatments: hCG injections are sometimes given to trigger ovulation during assisted reproductive procedures, like IVF.
👉Find out more: How long does it take to get pregnant after sex: Understanding the timeline
Which hormone is responsible for ovulation?
So, primarily, what hormone triggers ovulation or which hormone is responsible for ovulation? The LH (luteinizing hormone) is the primary and major hormone responsible for ovulation. As soon as the developing egg follicles mature in the ovary and become dominant, a sudden increase in LH levels triggers ovulation. An LH surge stimulates the ovaries and causes the dominant follicles to release an egg, which travels to the fallopian tubes.
The LH surge is the most fertile period as your ovaries release an egg that is ready to be fertilized. The egg remains viable up to 24 hours after releasing from the ovary, during which conception is possible. After this time, the egg ruptures and releases out of the body through menstruation.
Hormones essential for getting pregnant
All four hormones, including LH, FSH, estrogen and progesterone, are hormones that affect fertility and are crucial for a successful pregnancy. FSH and LH hormones help in ovulation, and low or high levels of these hormones can cause premature ovulation or anovulation, reducing the chances of a successful implantation.
A low estrogen and FSH hormone level can reduce follicle growth and prevent it from developing into a mature egg, affecting ovulation and fertilization.
Progesterone prepares the uterine lining for embryo growth and development, and disrupted levels of progesterone can impair the thickening of the uterine lining to an acceptable level, affecting the growth of an embryo.
How to balance hormones for fertility
Having regular and proper menstruation every month is a strong indicator of your hormonal health. It means all fertility hormones are released in your body correctly, resulting in ovulation, endometrial thickening and menstruation. So, as soon as a healthy sperm reaches your egg during ovulation, it will lead to fertilization and pregnancy.
Here are some natural ways to balance your fertility hormones:
Diet: Focus on a Mediterranean-style diet with vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and healthy fats while avoiding sugary, high-carb, and processed foods. This helps regulate estrogen and progesterone levels.
Exercise: Moderate-intensity exercises like walking, jogging, and yoga improve circulation and egg quality, boosting fertility.
Lifestyle modifications: Avoid smoking, limit alcohol, and reduce exposure to harmful toxins to support reproductive health.
Factors that can disrupt fertility hormones
The following factors can disrupt fertility hormones:
- Lifestyle factors including poor diet, smoking, alcohol abuse and stress.
- Environmental factors including exposure to toxins and chemicals.
- Certain medical conditions, like PCOS, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism, can disrupt fertility hormones and lead to infertility if the condition persists or remains untreated.
- Age: As a woman reaches 35 years old, her fertility begins to decline, which can affect the egg quality and quantity, causing problems in conceiving.
Factors that can disrupt fertility hormones
Testing your fertility hormones is essential for understanding your reproductive health. There are several tests that can help assess the levels of key hormones involved in fertility:
FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone): This test measures the level of FSH in your blood. High FSH levels on day 3 of your menstrual cycle can indicate diminished ovarian reserve.
LH (luteinizing hormone): LH is crucial for ovulation. A blood test can determine if ovulation is happening regularly, with an LH surge occurring just before ovulation.
Estradiol (estrogen): Estrogen levels are important for the development of eggs. A blood test is usually done early in your cycle to assess estrogen levels and monitor ovarian function.
Progesterone: A blood test is done after ovulation to determine if progesterone is being produced, which is essential for maintaining pregnancy.
AMH (Anti-müllerian hormone): AMH levels can give an indication of your ovarian reserve, helping to predict fertility potential. It’s particularly helpful for women who are considering IVF.
Thyroid tests: Thyroid function can impact fertility, so testing for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels is often recommended.
Prolactin: High levels of prolactin can interfere with ovulation, and a blood test can measure its levels.
These tests are typically ordered by a healthcare provider, and interpreting the results requires considering various factors like age, menstrual cycle, and overall health. If you’re concerned about your fertility, consult a doctor to determine the appropriate tests and next steps.
When to consult a doctor about fertility hormones
It is ideal to consult your healthcare provider about your fertility hormones if:
- You have irregular periods, no periods, or very painful periods, and symptoms like excessive hair growth, weight changes and acne.
- You are 35 or older and have been trying to conceive for over a year.
- You have been diagnosed with any female reproductive disorders, like endometriosis, PCOS, sexually transmitted infections, cervical cancer, or others and are experiencing problems in conceiving.
Your doctor may recommend fertility treatments depending on your condition. The three standard treatment options for infertility include medicines like clomiphene or gonadotropins to stimulate ovulation, surgical procedures to correct the cause of infertility, or assisted conception, like in-vitro fertilization.
Try Femia’s plan that helps remove your blocks to get pregnant
Questions from the Femia community
Is it possible to track my fertility hormones at home?
Yes, certain methods are available that can help you track your fertility hormones at home, like follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) tests and ovulation predictor kits that use strips to detect your fertility hormones.
How does thyroid health affect my fertility hormones?
Your thyroid gland produces essential hormones, like T3 and T4, which control the body's metabolism, growth, and development and indirectly regulate FSH and LH production. Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough T3 and T4 hormones, which affects ovulation and can lead to infertility.
Can birth control impact my fertility hormones long-term?
No, the use of birth control pills or any form of contraceptive doesn't impact your fertility for the long term, regardless of the duration of use. It can alter your hormonal levels or dysregulate your menstrual cycle for a short period, which returns to normal within a few weeks of stopping the contraception.
What role does insulin play in fertility hormones?
Insulin resistance affects female fertility by activating oxidative stress, which interferes with hormone secretion, oocyte development, energy metabolism, and embryo quality and implantation.
The bottom line
Our fertility hormones are involved in each stage of the reproductive cycle. The LH and FSH hormones help develop follicles within the ovaries and stimulate ovulation, while estrogen and progesterone prepare the uterine lining for implantation and embryo development.
A dysregulation in the levels of any of these hormones can impact ovulation, affecting the female’s ability to conceive. Luckily, various lifestyle changes, like following specific diets, like the Mediterranean diet, moderate exercise and yoga, limiting alcohol and smoking and adding supplements to balance hormones for fertility, can help restore hormonal balance and enhance fertility. Using an app to track fertility windows can help you monitor ovulation and identify the optimal time for trying to conceive.
However, it is essential to consult your healthcare provider for an individualized checkup before you start any supplement, especially if you experience symptoms like an irregular menstrual cycle, weight changes, increased sensitivity to cold or heat, fatigue, depression, or changes in bowel movement, as they may be a sign of hormonal imbalance.
References
- Cleveland Clinic. “Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH).” Cleveland Clinic, 20 Sept. 2024, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/24638-follicle-stimulating-hormone-fsh.
- Skoracka, Kinga, et al. “Female Fertility and the Nutritional Approach: The Most Essential Aspects.” Advances in Nutrition, vol. 12, no. 6, May 2021, pp. 2372–86, https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmab068.
- Mayo Clinic. “5 Lifestyle Choices That Can Affect Being Able to Get Pregnant.” Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/female-fertility/art-20045887.
- Girum, Tadele, and Abebaw Wasie. “Return of Fertility after Discontinuation of Contraception: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” Contraception and Reproductive Medicine, vol. 3, no. 1, May 2018, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40834-018-0064-y.
- Lei, Ruobing, et al. “Advances in the Study of the Correlation between Insulin Resistance and Infertility.” Frontiers in Endocrinology, vol. 15, Jan. 2024, https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1288326.
- National Health Service (NHS). “Treatment.” NHS, 11 Mar. 2024, www.nhs.uk/conditions/infertility/treatment.
- Mayo Clinic. “Infertility – Symptoms and Causes.” Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/infertility/symptoms-causes/syc-20354317.
- “The Impact of Exercise on Fertility.” Krishna Medical Centre, www.krishnamedicalcentre.org/blog/the-impact-of-exercise-on-fertility#:~:text=Research%20indicates%20that%20women%20engaging,compared%20to%20less%20active%20men.
At 36 weeks pregnant, your baby is nearly early-term and preparing for birth. Learn about symptoms, delivery readiness, and labor tips.

Many wonder, is it safe to dye your hair while pregnant? You can take precautions to protect yourself and your developing baby from chemical exposure.
Does stomach pain after sex mean you are pregnant? Learn if it’s a sign of pregnancy or other health concerns. Understand the causes, symptoms, and when to seek medical advice.
