Femia > Health Library > Your cycle > Health > Low testosterone in women: Symptoms, causes, and how to treat it
Low testosterone in women: Symptoms, causes, and how to treat it

- Updated Feb 11, 2025
- Published
CRAFTED BY HUMAN
Crafted by human At Femia, we provide accurate and up-to-date information at every stage of your journey, from trying to conceive, pregnancy and postnatal support. All content is created by a real person based on in-depth research and own professional experience. Femia ensures that you will receive expert advice, strict accuracy and a personalized approach from our authors/medical experts. Learn more about our editorial policy.
FACT CHECKED
Fact checked At Femia Health, we maintain the highest standards of editorial excellence in delivering content focused on helping you conceive, guiding you through pregnancy, and supporting you postpartum. Explore our content review principles to learn how we ensure the accuracy and quality of our health and lifestyle tips for every stage of your journey.
- Testosterone is primarily a male sex hormone, but it is also present in females in lower amounts. It is involved in maintaining a woman’s sexual desires and mental and physical health.
- Low testosterone in women can cause symptoms like decreased sex drive, depression or mood swings, and reduced muscle strength, bone density, and fatigue.
- The causes of low testosterone in females include age, surgical removal of ovaries, and underlying medical conditions like adrenal insufficiency, ovarian failure, hormonal imbalance, and malnutrition.
- Low testosterone can be treated in females by lifestyle changes, treating underlying medical conditions, and testosterone therapy.
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, is necessary for both male and female health. It is primarily involved in developing male sex characteristics but also maintains various body processes in females like bone and muscle health, mood, and libido.
While testosterone is often associated with men, it is also crucial for female health. Low levels of testosterone can cause a variety of symptoms in women, including depression, low libido, fatigue, and more. Let’s discuss the role, causes, symptoms, and treatment of low testosterone in women in detail.
Femia helps millions of women understand and balance their hormones
What role does testosterone play in the female body?
So, what role does testosterone play in the female body, or is it only important for males?
Testosterone is involved in many important bodily functions in females. From maintaining physical and mental health to contributing to hormonal balance and ovarian function, testosterone is necessary for a woman’s overall physical, reproductive, sexual, and emotional well-being.
The functions of testosterone in females include:
1. Energy and mood
Testosterone helps reuptake serotonin, the “happy” neurotransmitter in the brain, improving overall mood, well-being, and energy in females.
2. Cognitive functions
Testosterone aids in improving cognitive functions and cognitive performance in women and men.
3. Hormone balance
A balance of testosterone hormone in females helps maintain the functioning of ovaries and other reproductive or fertility hormones, like estrogen and progesterone.
4. Sexual response
In both females and males, testosterone is involved in maintaining sexual response. It stimulates sexual desire, arousal, orgasm, and overall sexual satisfaction.
5. Muscle and bone health
Testosterone is also involved in stimulating muscle growth and bone formation by activating osteoblasts and preventing bone loss.
👉Find out more: Estrogen and progesterone: Functions, differences, and why they matter
Female testosterone levels by age
The normal female testosterone levels by age are:
- 1-9 years: The testosterone level in children or young females is the lowest. In ages 1-9, testosterone levels in females are typically 2.5–10 ng/dL.
- 10-40 years: The testosterone level in females begins to increase when they reach puberty and is at its highest level during their reproductive years, which commonly lasts to the end of the 30s or mid-40s. Testosterone levels in females aged 10-39 or 40 years fluctuate between 15-70 ng/dL.
- 45-55 years: After menopause, typically between the ages of 45 and 55, the testosterone level in females begins to decline at a faster rate. The levels of testosterone in females aged 45 to 55 years are commonly between 9 to 55 ng/dL.
Symptoms of low testosterone in women
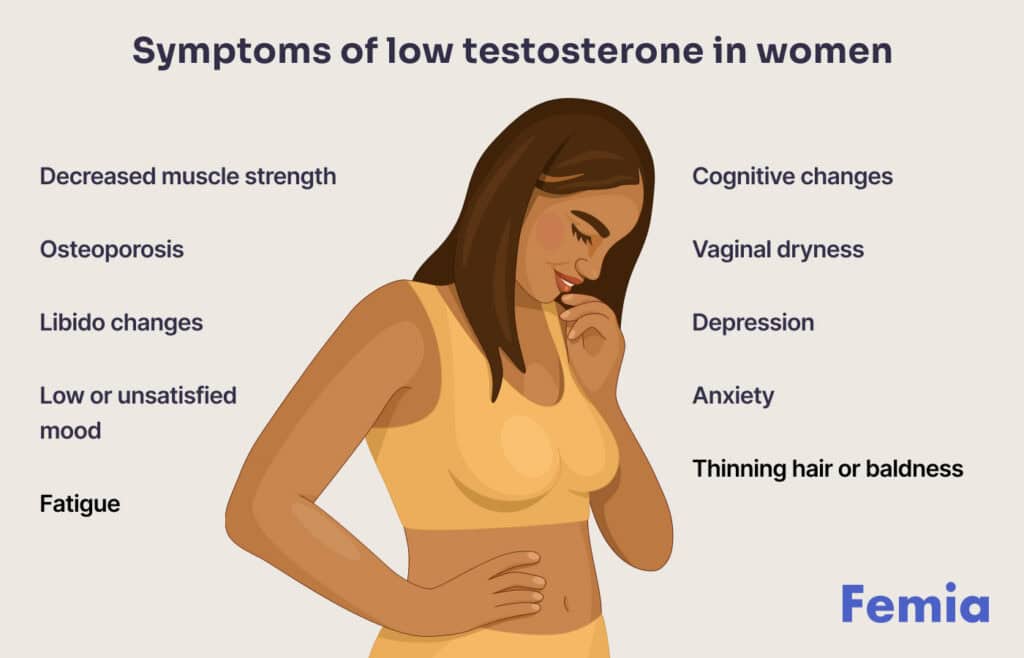
The signs of low testosterone in women include:
- Decreased muscle strength
- Osteoporosis
- Changes in sexual functions, including low sex drive and reduced sexual desire. The primary indication or one of the most common symptoms of low testosterone in women is decreased libido.
- Low or unsatisfied mood
- Fatigue
- Changes in cognitive functions, like reduced thinking ability.
- Vaginal dryness
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Thinning hair or baldness
What causes low testosterone in women?
So, what causes low testosterone in women? Let’s discuss them in detail.
1. Age
The major cause of low testosterone in women is age. When a female reaches 30 years, testosterone levels start to decline by 1% each year.
Hence, as a result of testosterone reduction with age, a woman may begin to experience low sex drive, mood swings, and other symptoms, like depression, fatigue, and more.
2. Menopause
The second major cause of low testosterone in women is menopause. By the time a female reaches menopause, testosterone decreases by 50% of its initial levels. So, during menopause, which typically appears between the ages of 45-50, the testosterone level begins to decline at a faster rate than ever before.
3. Ovarian disease or ovary removal
The removal of ovaries due to cancer or other disease, like ovarian failure, may also cause low testosterone in women, as a female’s ovaries are responsible for producing around 25% of the body’s testosterone.
4. Malnutrition
A healthy diet is necessary for maintaining hormonal balance. An unhealthy diet may lead to hormonal imbalance through insulin sensitivity, inflammation, and stress on the adrenal glands.
Hence, inadequate nutrition, including intake of vitamins and proteins can impair testosterone output and cause low testosterone levels in females.
5. Medications
Several medications can also cause low testosterone in females as a side effect, like birth control pills, long-term use of corticosteroids, oral estrogen, statins, and opioids.
Femia helps millions of women understand and balance their hormones
How to treat low testosterone in females
The treatment options for low testosterone in women include:
1. Lifestyle changes
Low testosterone can be improved with a healthy diet and lifestyle. For example, regular 30-minute moderate-intensity exercise, maintaining a healthy diet enriched with vitamins, vegetables, fruits, eggs, red meat, and fatty fish; and limiting carbohydrate, alcohol, and calorie intake can help boost your overall hormonal profile and improve low testosterone.
Moreover, ensuring a sound, full night’s sleep and taking measures to reduce stress with stress-reducing practices, like meditation, yoga, and mindfulness, is crucial to improving your overall hormonal balance and testosterone levels.
2. Treating underlying conditions
Many underlying conditions, like side effects from medications, ovarian disease, adrenal disorders, and other hormonal imbalances, can cause low testosterone levels.
Hence, it is crucial to give thought to both your reproductive health and overall health. An underlying disease could be responsible for a low level of testosterone.
3. Testosterone therapy
Testosterone therapy or hormone replacement therapy contains testosterone that is administered in the form of drugs like patches, injections, and gels to replenish the low levels of testosterone in the body.
It is typically administered when the condition is severe and the symptoms of low testosterone become persistent and unbearable or interfere with the quality of life.
Excessive testosterone can cause male-related side effects in women. You should consult your healthcare provider to determine the safest and most effective treatment method for low testosterone.
👉Find out more: How many eggs does a woman have? Understanding egg count and fertility by age
Testosterone side effects in women
As testosterone is primarily a male sex hormone, its excessive levels in females can lead to many unwanted or male-related side effects. Hence, proper monitoring is crucial when treating low testosterone in women.
The side effects of testosterone in women or the risk of excessive testosterone therapy can include:
- A deeper voice
- Excessive body hair
- Skin changes, like acne or oily skin.
- Weight gain
- Mood swings, anxiety, irritability, or depression.
- Swelling in the hands or feet.
- Breast swelling
- No periods
When to see a doctor
Moderate but bearable changes in mood, sex drive, and physical health are normal while experiencing a low testosterone level with age.
However, if you are still in your reproductive years, i.e., below 40, and experience symptoms of low testosterone, or if they become intense, unbearable, and interfere with your daily life, it is crucial to consult your doctor.
Low testosterone levels can be diagnosed through testosterone blood tests and evaluating low testosterone symptoms in women, like decreased sex drive, hot flashes, fatigue, loss of hair, etc.
Questions from the Femia community
Does menopause cause low testosterone?
Yes, with age, the testosterone level decreases, and by the time a woman reaches menopause, the testosterone level halves.
Can high stress cause low testosterone in women?
Yes. High stress can increase the production of the stress hormone cortisol, which can cause mood changes, reduced sex drive, and irregular periods. Moreover, high cortisol levels from chronic and persistent stress can also disrupt the balance of reproductive hormones and cause low testosterone in women.
Are there natural ways to boost women’s testosterone levels?
Yes, dietary and lifestyle changes can help boost testosterone levels in women. For example, taking steps to manage stress; increasing vitamin D intake with foods – like egg yolks, red meat, liver, and oily fish, like salmon, sardines, and mackerel – maintaining adequate 8-hour daily sleep; and exercising for 30-45 minutes daily,, can help boost a women’s testosterone level.
How is low testosterone diagnosed in women?
Testosterone can be diagnosed with a blood test that shows the total testosterone level in your blood and by evaluating symptoms of low testosterone, like mood changes, reduced sex drive, and fatigue.
The bottom line
Testosterone is a male sex hormone, but it plays a crucial role in maintaining a woman’s overall health – helping with things like energy, mood, libido, cognition and more.
Low testosterone in women can cause symptoms like mood changes, depression, decreased sex drive, fatigue, and hot flashes. Hence, it is important to treat low testosterone in women. This can be done with lifestyle and dietary changes, by addressing underlying medical conditions, and balancing hormones for good physical and mental health.
References
- Scott, Alice, and Louise Newson. “Should We Be Prescribing Testosterone to Perimenopausal and Menopausal Women? A Guide to Prescribing Testosterone for Women in Primary Care.” British Journal of General Practice, vol. 70, no. 693, Mar. 2020, pp. 203–04. https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp20x709265.
- “Testosterone Therapy: Potential Benefits and Risks as You Age.” Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/sexual-health/in-depth/testosterone-therapy/art-20045728.
- PubMed, 1 Sept. 2004, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15509090.
- Brownlee, Kaye K., et al. “Relationship Between Circulating Cortisol and Testosterone: Influence of Physical Exercise.” 1 Mar. 2005, PMC, pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3880087.
Kansas has filed a lawsuit against Pfizer, alleging misinformation about its COVID-19 vaccine’s safety and effectiveness, including during pregnancy. Learn more about the claims, evidence, and implications.
At 3 weeks pregnant, your body begins showing early pregnancy signs. Explore 3-week symptoms, fetal growth, and tips for this early stage.

A coregasm is an exercise-induced orgasm that occurs during an intense core workout. An orgasm while working out is an asexual bodily response to exercise.

