Femia > Health Library > Your cycle > Sex > What are the chances of getting pregnant from precum while ovulating?
What are the chances of getting pregnant from precum while ovulating?

- Updated Mar 2, 2025
- Published
CRAFTED BY HUMAN
Crafted by human At Femia, we provide accurate and up-to-date information at every stage of your journey, from trying to conceive, pregnancy and postnatal support. All content is created by a real person based on in-depth research and own professional experience. Femia ensures that you will receive expert advice, strict accuracy and a personalized approach from our authors/medical experts. Learn more about our editorial policy.
FACT CHECKED
Fact checked At Femia Health, we maintain the highest standards of editorial excellence in delivering content focused on helping you conceive, guiding you through pregnancy, and supporting you postpartum. Explore our content review principles to learn how we ensure the accuracy and quality of our health and lifestyle tips for every stage of your journey.
Sperm may be present in precum, resulting in pregnancy if you are ovulating. Your chances of pregnancy with precum rely on numerous factors including whether or not you are using a form of contraception, how many sperm is presented in precum, and if that sperm can make its way to the egg during ovulation.
With regular unprotected sex, you always have a chance of getting pregnant. This chance increases if you are having sex in your fertile window, which includes the day of ovulation. Precum, is an involuntary secretion, which can contain sperm, sometimes from a previous ejaculate. While the number of sperm is low, these sperm can travel into the uterus and result in conception if you are ovulating. However, your chances of getting pregnant vary significantly based on several factors which we will explore further in this article.
Can you get pregnant from precum?
Pre-ejaculatory fluid, what we call precum, is a clear fluid released from the penis by small glands near the urethra following arousal. It is an involuntary secretion noticed during sex, before a more voluntary ejaculation. Precum works as a lubricant favoring the movement of sperm into the vagina.
A small study showed that 41% of their subjects had sperm in their pre-ejaculate. Of this, 37% had motile sperm, which means they have the potential to travel through the uterus to reach the egg. In another study, only 16.7% of their participants had active motile sperm in their pre-ejaculates. While this doesn’t accurately predict whether every secretion of precum has motile sperm, these estimates are sufficient to enlighten the possibility of having sperm in precum.
Sperm in precum can remain from a recent ejaculation. Additionally, some men might consistently release sperm with their precum.
If you have unprotected intercourse during your fertile window (5 days prior to ovulation plus the day of ovulation) and are only exposed to precum, pregnancy may still be possible, even if the chances are small. If you do not wish to get pregnant and are not using hormonal birth control, using a barrier method of contraception, such as a male or female condom, can reduce your chances.
@femia.fertility Track your v discharge with Femia tracker to know when you have the highest chances of conceiving a baby. Link in bio!#ovulation #ovulationsymptoms #ttccommunity #fertilityawareness #expertadvice #ttc #fertilitytracker #highfertility #womenshealth #health #learnontiktok #periodtok ♬ original sound - Femia fertility tracker
How likely is it to get pregnant from precum while ovulating?
Pregnancy is possible if unprotected vaginal-penile sex happen during the 5 days prior to ovulation plus the day of ovulation. This is because sperm can service in the tubes of the uterus for up to 5 days.
To reliably predict your fertility window, the duration during which you have the highest chances of getting pregnant, you need to regularly track your menstrual cycles. Along with logging your period dates, add physical symptoms you notice throughout your cycle, specifically around ovulation, such as a rise in body temperature, increased cervical mucus secretion, or lower pelvic cramps. Your fertile window is about 5-7 days every cycle.
👉Find out more: Can you get pregnant after your period? Understanding your fertility window
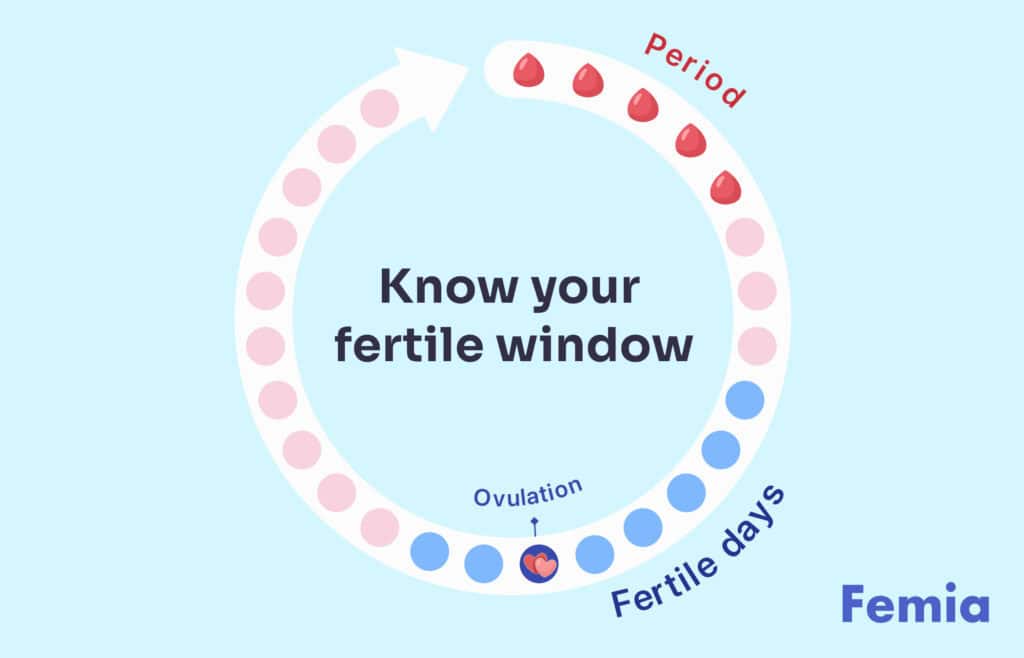
By day 12 of your cycle you have a 58% chance of being in your fertile window if you have a typical 28 day cycle. This lowers to about less than 1% by day 28. This means having sex every other day in your fertile window increases your chances of getting pregnant.
Having only been exposed to precum during the fertile window, while a low chance, still poses a risk of getting pregnant. This likelihood differs based on various circumstances and phases of your menstrual cycle.
| Condition during sex | Chances of getting pregnant with sperm in precum |
|---|---|
| You are in your fertile window | Your fertile window is roughly 5-7 days of your menstrual cycle. You are most likely to get pregnant from unprotected intercourse, 2 days before and on your ovulation day. |
| You are on your period | While there is a less than 1% chance of being in your fertile window while on your period, this increases to 10% by day 6. Your chance of getting pregnant is highest if you have long periods and short cycles. |
| You use a condom or other barrier methods | With correct use, pregnancy protection is 98% for male condoms and 95% for female condoms. This is much lower in reality with common use, especially if condoms are used after precum is released or if they break during sex. |
| You are on hormonal birth control | Various forms of hormonal birth control can reliably prevent pregnancy, only if used correctly and as prescribed. |
| You have an IUD | An IUD’s failure rate is about 1-2 pregnancies per 100 women-years, which is about 1%. However, there are higher chances of tubal pregnancy, if sperm reaches an egg during ovulation. |
| Your partner has had a vasectomy | A survey of urologists concluded that the highest chances of pregnancy are the first few months after a vasectomy. This reduced to 1 pregnancy in 1000 2.5 years after the procedure. |
Under most of these conditions, pregnancy is only possible if sperm is released in the precum. This means the chances of getting pregnant from precum while you are ovulating are low but still possible.
👉Find out more: How long does it take to get pregnant after IUD removal?
At other times in your cycle
One of the main issues with tracking your cycle for family planning is that mistakes can happen. Sometimes, your cycle may be shorter than expected, meaning your fertile window happens sooner than usual, which could potentially leave you unprotected during sex.
A study published in the British Medical Journal in 2000 analyzed the reproductive cycles of over 200 women. The researchers found that there were very few days in each cycle where there was no risk of pregnancy and concluded that calendar methods are not entirely effective forms of contraception. While theoretically, you should be safe from pregnancy outside your fertile window, it’s not easy to successfully determine when that will be, and this leaves you exposed to the risk of unplanned pregnancy.
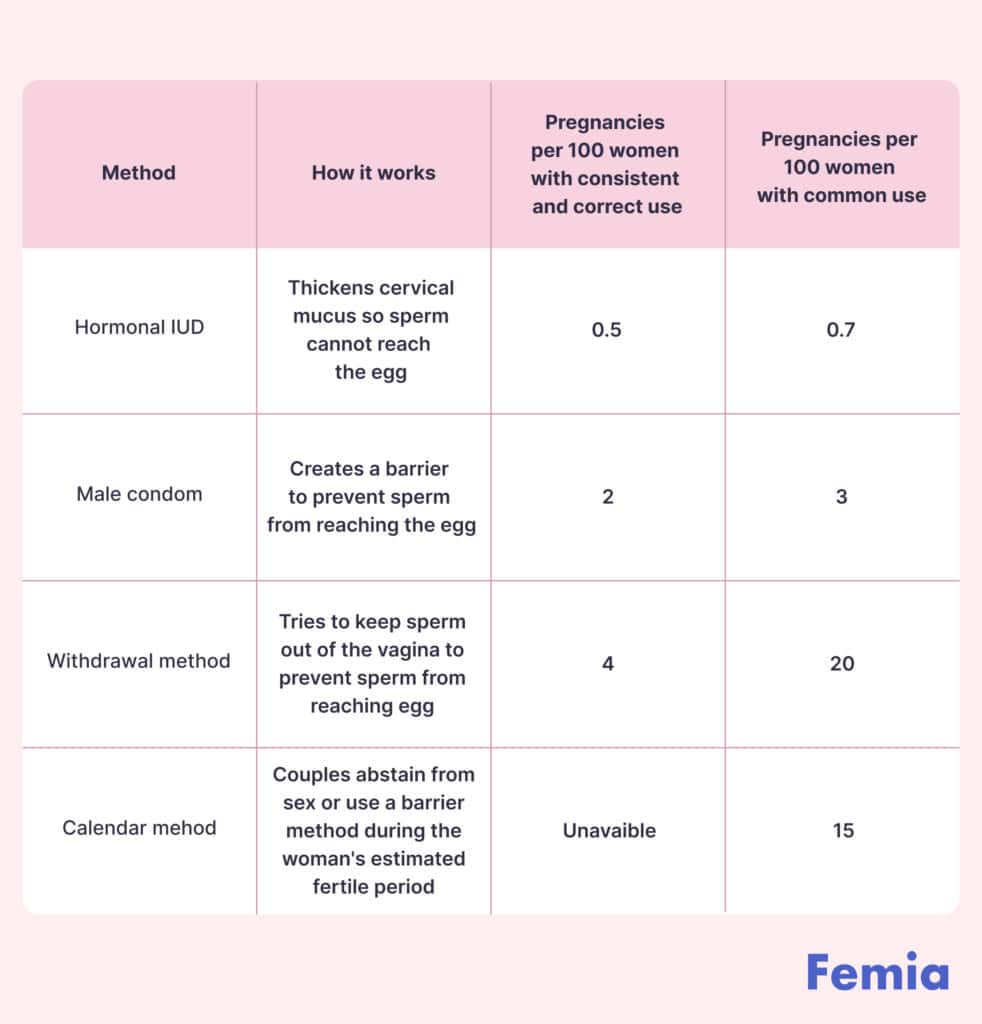
Source: World Health Organization
Can you get pregnant if only the tip goes in?
With unprotected intercourse, you have a chance of getting pregnant if activity occurs in the fertile window, even if only the tip of the penis goes in. However, this is very low probability compared to when there is full penetration deep inside the vagina.
It is crucial to remember that precum is not a voluntary secretion, which means it is possible your partner may not even be aware of its release. Plus, this fluid may leak from the tip of the penis even before full erection. As we have discussed earlier, sperm can leak into the precum which can make its way to the vagina, if the tip lies at the entrance of your vagina.
While under these circumstances the chances of getting pregnant are extremely low, it is still definitely possible, more so if you are ovulating.
👉Find out more: How soon after unprotected sex can I test for pregnancy?
Can a woman get pregnant without sperm entering her body?
The absence of sperm in an ejaculate is observed in about 1% of all men. This is called azoospermia and is one cause of male infertility. But this is rare, again, occurring in only about 1% of biologic males. Many factors contribute to whether the sperm is able to fertilize the egg and lead to conception, such as the number of sperm in the ejaculate, motility, and quality. But all healthy motile sperm are capable of conception, even if they are found in precum.
It is a common misconception that precum does not contain sperm, and does not lead to pregnancy even if you are ovulating. This is frequently a reason why the pull-out method is used for regular contraception. However, as we have seen above, sperm can be present in precum, making the pull-out method inefficient in preventing pregnancy from precum while ovulating.

Should I take emergency contraception?
Since there is a chance, even a small one, of getting pregnant with precum, taking emergency contraception would be the next step if you do not wish to get pregnant.
Your highest chance of pregnancy with precum is if you are in your fertile window. While it can be possible to skip the emergency contraception outside this window, taking the “morning after” pill after unprotected sex is recommended if you do not wish to get pregnant.
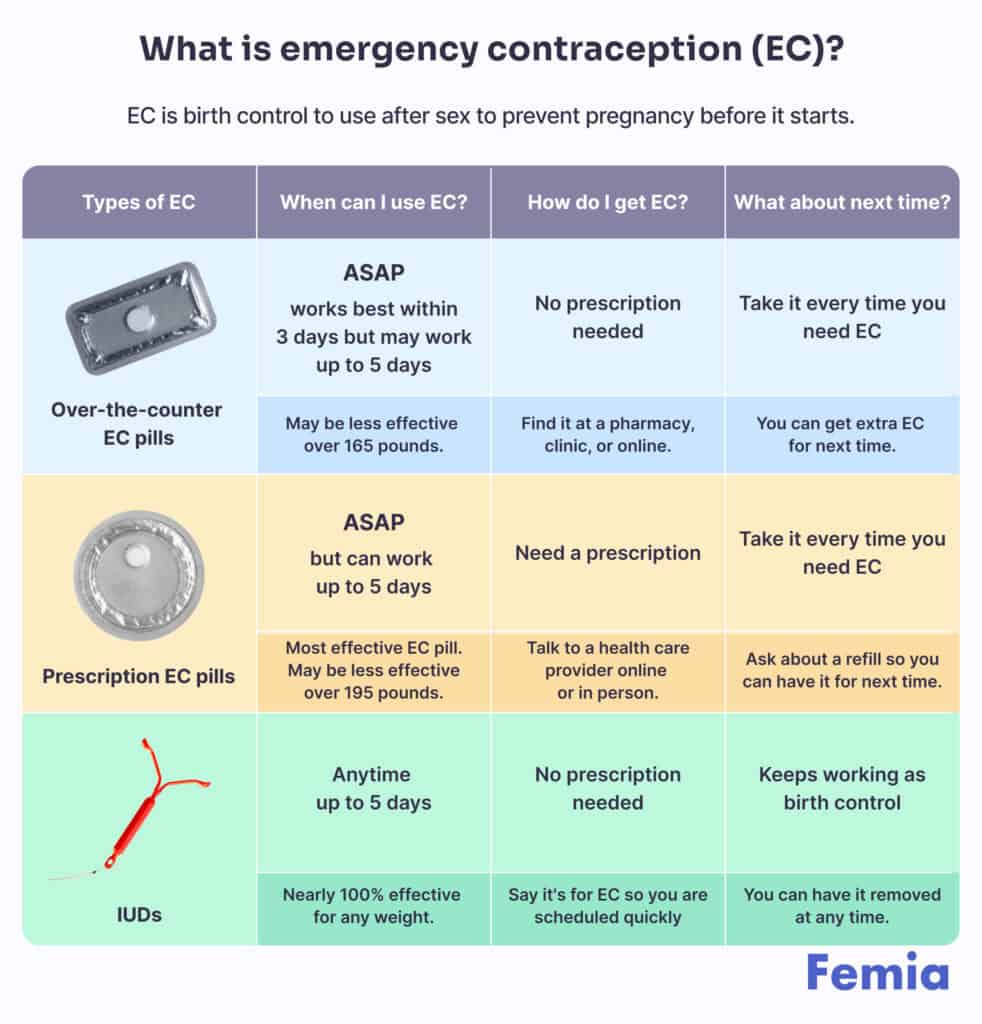
Emergency contraception can prevent 95% of pregnancies if taken within 5 days of unprotected sex. It is also effective with sperm released in pre-ejaculate.
The two commonly used methods of emergency contraception are emergency contraceptive pills and copper intrauterine devices. One type of oral emergency contraception is available over the counter (without a prescription) and may be taken up to 72 hours after the act, but sooner is better. If you are unsure of which is the most suitable for you, consult with your healthcare provider.
When can I take a home pregnancy test?
If you feel you could have become pregnant from a recent sexual encounter you will want to confirm this. The easiest way to do this is with a home pregnancy test.
Following the fertilization of an egg with sperm, it takes about a week to travel and implant into the uterus. Once implanted, it slowly starts releasing the hCG hormone, which is detected by home urine pregnancy kits. While the amount of hormone increases significantly after implantation, detectable levels indicating pregnancy are noticed after you have missed your period.
You may have a false negative test if you check too soon after sex. Most clinicians recommend checking for pregnancy once your period is late or at the earliest, about 2 days prior to your next expected period. If you wish to confirm pregnancy sooner, you can take a blood test at your doctor’s office, which can detect hCG levels earlier than a urine pregnancy test. However, this is rarely needed.
Questions from the Femia community
How effective is the pull-out method in preventing pregnancy?
It is estimated that 1 in 5 women can get pregnant using the pull-out method as their primary method of contraception. The withdrawal method is least effective in preventing pregnancydue to sperm present in precum, as this fluid is an involuntary secretion. Precum can be released into the vagina even before a man pulls out during sex.
Is it safe to rely on the pull-out method during ovulation?
Since the pull-out method is the least effective method of contraception, it results in the highest failure rate. This means more women are likely to get pregnant using the pull-out method for contraception, than using other forms of contraception. Your chances of getting pregnant are highest if you are within 2 days of ovulation but pregnancy may occur up to 5 days prior to ovulation as sperm can live that long in the fallopian tubes (the fertile window).
How often can precum cause pregnancy during ovulation?
Sperm is not always present in pre-ejaculatory fluid. In the occasional incident that it is, sperm in precum is capable of resulting in pregnancy, provided it makes its way to the uterus, and you are ovulating or about to ovulate in a day or two. Since the presence of sperm in precum is not always consistent, the chances are low even if you are ovulating.
Can precum on fingers cause pregnancy?
The chance is extremely low for the transfer of sperm from fingers into your vagina, but it is not zero. You can still get pregnant if any viable sperm passes into your vagina, and the chances are higher if you are ovulating and have full penile-vaginal penetration.
Does the presence of sperm in precum vary from person to person?
Yes, the presence and amount of sperm in the precum can vary from person to person. Not all pre-ejaculatory fluid contains sperm. Even if it does, only a small percentage are motile sperm capable of leading to pregnancy. Since the presence of sperm is unreliable, using some form of reliable contraception can lower your chances of getting pregnant with precum.
The bottom line
While low, it is possible to pregnant with precum, especially if you are ovulating. Pre-ejaculatory fluid is released when aroused and facilitates lubrication during intercourse. Sperm can make its way into precum as it is released. This sperm is capable of fertilizing an egg released durinaround the time of ovulation. Using reliable contraception can help prevent pregnancy with precum. If you feel you might have become pregnant following unprotected sex, consult with your doctor to know your options and receive individualized care including emergency contraception as needed.
References
- Killick, Stephen R., et al. “Sperm Content of Pre-ejaculatory Fluid.” Human Fertility, vol. 14, no. 1, Dec. 2010, pp. 48–52. https://doi.org/10.3109/14647273.2010.520798.
- Kovavisarach, Ekachai et al. “Presence of Sperm in Pre-Ejaculatory Fluid of Healthy Males.” Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand = Chotmaihet thangphaet vol. 99 Suppl 2 (2016): S38-41.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27266214/.
- Stirnemann, Julien J., et al. “Day-specific Probabilities of Conception in Fertile Cycles Resulting in Spontaneous Pregnancies.” Human Reproduction, vol. 28, no. 4, Jan. 2013, pp. 1110–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/des449.
- Suarez, S. S., and A. A. Pacey. “Sperm Transport in the Female Reproductive Tract.” Human Reproduction Update, vol. 12, no. 1, Nov. 2005, pp. 23–37. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmi047.
- Johnson, Sarah, et al. “Increased Likelihood of Pregnancy From Sex on the Two Days Before Ovulation [5B].” Obstetrics and Gynecology (New York. 1953. Online)/Obstetrics and Gynecology, vol. 131, no. 1, May 2018, p. 20S. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.aog.0000532907.57204.dd.
- Wilcox, A. J. “The Timing of the ‘Fertile Window’ in the Menstrual Cycle: Day Specific Estimates From a Prospective Study.” BMJ. British Medical Journal, vol. 321, no. 7271, Nov. 2000, pp. 1259–62. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.321.7271.1259.
- Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). “Contraception: Hormonal Contraceptives.” InformedHealth.org – NCBI Bookshelf, 29 June 2017, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441576.
- Beksinska, Mags, et al. “Male and Female Condoms: Their Key Role in Pregnancy and STI/HIV Prevention.” Baillière’s Best Practice & Research. Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology/Baillière’s Best Practice and Research in Clinical Obstetrics and Gynaecology, vol. 66, July 2020, pp. 55–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2019.12.001.
- Elvin, Piriyev, and Römer Thomas. “Case Report: Pregnancy While Using an IUD.” Obstetrics and Gynaecology Cases – Reviews, vol. 7, no. 5, Sept. 2020, https://doi.org/10.23937/2377-9004/1410172.
- Deneux-Tharaux, Catherine, et al. “Pregnancy Rates After Vasectomy: A Survey of US Urologists.” Contraception, vol. 69, no. 5, May 2004, pp. 401–06. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2003.12.009.
- World Health Organization: WHO. Emergency Contraception. 9 Nov. 2021, www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/emergency-contraception.

Experiencing third trimester nausea? Learn what causes it, how to find relief, and when to consult a doctor. Discover tips to stop feeling sick in late pregnancy.
At 39 weeks pregnant, your baby is ready to arrive. Learn about labor signs, discharge, and tips for managing delivery anxiety.
Let’s learn how long does it take for sperm to reach an egg, when implantation happens and factors affecting the speed.

